Cities have prioritised the uptake of low-carbon and unconventional sources of energy, found the CPR study
New Delhi: The government has earmarked spending Rs 13,161 crore for energy projects being implemented under the Smart Cities Mission (SCM) with most of the funds dedicated to developing basic infrastructure for enhancing the grid and supply. Also, solar rooftop projects will account for around a half of this expenditure, according to a study.
“Cities have also proposed projects in solar energy, electric vehicles, waste-to-energy and Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting, indicating their appetite for low-carbon projects,” the report by Centre for Policy Research (CPR) said.
It focuses on the low carbon transition of India’s smart cities and is based on a database of projects and financing plans submitted by the first 60 cities selected under the first three phases of the SCM, an urban scheme launched by the centre in 2015.
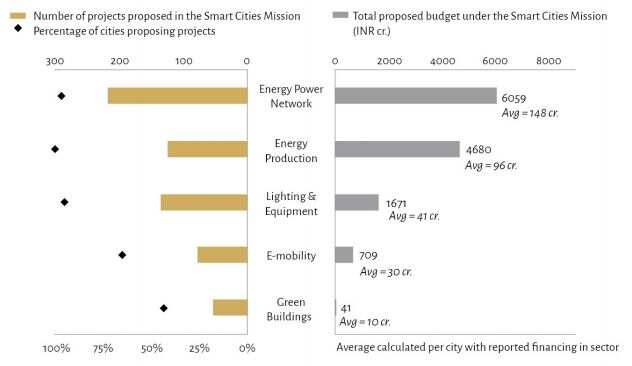
CPR found all the cities have emphasised on investing in energy distribution and supply infrastructure, with 81 per cent of all funds dedicated to these two sectors alone.
“Nearly 50 per cent of the investments are budgeted for energy distribution networks. This category has the highest total budget across the 60 cities which is Rs 6,059 crore and the highest number of proposed components,” said the report. Most of the investment was found to be proposed for upgrading the distribution network such as underground wiring and improvement of power sub-stations.
Cities also considered the deployment of smart-grid projects with municipalities considering smart meters and smart grid systems.
The sector with the second-highest committed investment was found to be energy production with projects worth Rs 4,680 crore. According to the study, cities prioritised the uptake of low-carbon and unconventional sources of energy and none of the proposed investments were found for conventional fossil fuels. “More than 50 per cent of components proposed are rooftop solar solutions and other types of solar installations,” said the report.
The remaining investments were found to be dedicated to demand-side measures like lighting & equipment, e-mobility and green buildings. Amongst the three, almost all cities proposed investments in lighting and equipment and few projects in e-mobility and green buildings.
Distribution of components and budget across categories. Percentage of cities that included projects per category:
Source: Centre for Policy Research
The report stated cities have the potential to foster innovative energy projects based on the linkages between carbon mitigation and local manufacturing. It called for clarity in institutional arrangements for cities to help enable the transition to low-carbon energy pathway.