
Solar panel fire season is all year round and it’s getting more intense in Australia
2020 was a bumper year for solar power in Australia. More solar PV systems were installed in the first nine months than in all of any previous year.
Almost one in four Australian houses now have rooftop solar panels. But the number of solar panel incidents reported by fire and emergency services has increased too.
Fire and Rescue NSW reportedly put out 30 blazes sparked by panels in just three months late last year.
The exponential growth in solar PV and associated problems has attracted media and political attention.
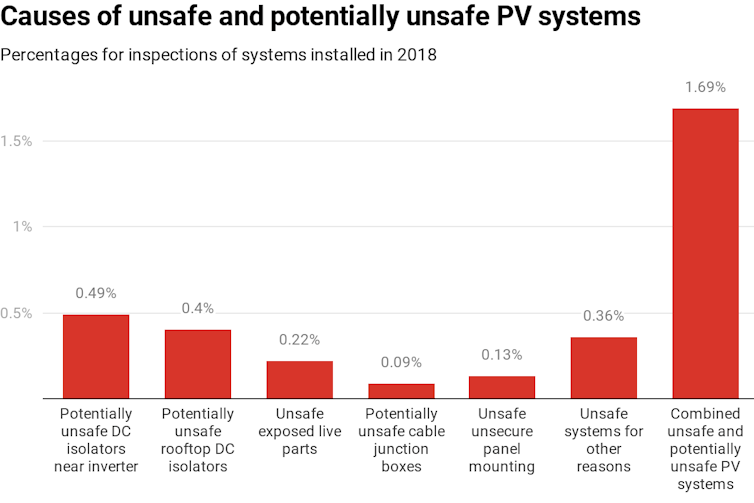
In 2018, federal Energy Minister Angus Taylor warned his state counterparts lives were at risk from substandard solar panel installations. An audit of the Clean Energy Regulator by the Australian National Audit Office found there were potentially tens of thousands of badly installed and even unsafe rooftop systems. The regulator had inspected just 1.2% of rooftop installations.
It’s a nationwide problem
State and territory regulators are responsible for electrical safety. Only Victoria mandates an inspection of each installed system.
Taylor announced an inquiry into the industry last August.
Last October, Fire and Rescue NSW Superintendent Graham Kingland said:
Components such as DC isolators and inverters, rather than the actual panels, are the cause of most solar-related fires. A DC isolator is a manually operated switch next to a solar panel array that shuts off DC current between the array and the inverter. It was intended as an extra safety mechanism, but the switches have caused more problems than they have solved – particularly when not installed correctly or when poor-quality components are used.
Solar is cheaper in Australia but poorly regulated
A recent report rated Australia as one of the cheapest per kilowatt for solar PV, but it questioned our safety standards. Most solar systems sold in Australia use DC voltages that can pose a serious fire risk.
Unfortunately, Australia has been slow to adopt safer solar regulations. In contrast, the United States has had safety standards preventing the installation of conventional DC solar systems since as early as 2014.
It’s more difficult for lower-voltage, microinverter-based systems (requiring no DC isolator switch) to catch fire, but it’s not impossible.
An amendment to the DC isolator standard (AS/NZS 5033:2014) to improve product datasheets and ensure isolators can withstand the harsh Australian climate took effect on June 28 2019. By then, over 2 million systems had been installed on Australian rooftops.
Added to issues such as flammable cladding, dodgy electrical cable and other “grey imports” (products not sourced from approved manufacturers) in the building industry, we are now playing a game of catch-up.
Poor-quality solar rooftop components have led to an expanding list of product recalls. The latest Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) recall list includes installations managed by industry giants such as Origin and AGL.
One notable recall in 2014 reported a risk of “arcing” and “eventual catastrophic failure, resulting in fire”. It listed no fewer than nine traders operating nationally as having used this failed product. The recall noted that the product supplier, Blueline Solar Pty Ltd, was insolvent.
Solar systems do not fall under the National Construction Code unless an ancillary structure is being created. Most systems are simply fixed with rails to an existing roof. If the code covered rooftop solar, this would require private certification and a compliance check on any system, as is the case overseas.
Research has shown consumers’ knowledge of solar systems is poor. Many owners have little idea if their system is working properly, or even at all.
And how would a consumer know what kind of DC isolator is on their roof or how to shut down the system in the event of a fire?
Solar panel systems are a growing incident category for firefighters. Yet even among firefighters there is some confusion on procedures to deal with a fire on live solar panels.

Even some firefighters aren’t clear about how to deal with fires on live solar panels.
Solar panel fires have yet to make it onto a top 10 list of domestic fire causes (statistically, your Christmas tree lights are a greater risk). But the sheer volume of installations and ageing components in uninspected older systems are increasing the risks.
One Aussie inventor has developed a product PVStop — “a spray-on solution to mitigate solar panel risks by reducing DC output to safe levels to offer homeowners and emergency personnel peace of mind”.
The latest update on Clean Energy Regulator inspections completed to June 30 2020 shows a negligible 0.05% decrease in substandard systems. Roughly one in 30 systems (3.1%) have been deemed unsafe and another 17.9% substandard.
Without adequate solar PV industry standards, tools, inspection regimes, procedures or training, dangerous scenarios may increasingly put lives at risk. The high uptake of solar is very good news for reducing household electricity bills and carbon emissions, but safety issues undermine these positives.
The surge in installations, the introduction of batteries, the ageing of panels and components together with more extreme weather events mean solar panel incidents are likely to continue increasing.
Australia prides itself on being a world leader in household solar but until now we have not fully appreciated the safety risks. Fire authorities would do well to update fire safety guides that omit specific information on solar. And system owners should ensure they understand the risks and shut-down procedures.















