What is National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHEM)? All about its significance, advantages and disadvantages here
Why in News?
It was in the Budget speech of this year that the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman included the introduction of National Hydrogen Energy Mission. The Government has also started holding Green Hydrogen auctions.
There are also talks to mandate the usage of 10% domestic hydrogen in fertilizer, steel and oil refineries.
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Industries to benefit
The end users are said to be steel, chemical and transportation industry. These contribute to one third of greenhouse gas emissions due to the amount of fossil fuels they burn, which can be directly replaced with hydrogen. Despite being said the hydrogen technology was not scaled up.
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Significance
- Hydrogen is said to be the alternative fuel and would replace fossil fuels
- India has set its goals to de-carbonize itself by 2050.
- This along with its ambitious goal of 175 GW of renewable energy capacity that was given impetus in the Union Budget 2021-22 would also get to raise INR 1500 crore finance
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Reason for implementation
- India’s heavy dependence on coal and the need to replace fossil fuels with hydrogen
- Since it is estimated hydrogen helped in the formation of Earth, it would be more abundant than Oxygen.
- The fuel would be used and can be reused again as it would control pollution.
- It is said to be 2-3 times better than petrol.
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Types of Hydrogen
- Green Hydrogen: It is produced from renewable resources of energy and not fossil fuels. The by products are water and water vapour
- Blue Hydrogen: It is sourced from fossil fuels. The emission or the by products such as CO2 and CO are stored. It is better than grey hydrogen.
- Grey Hydrogen: India’s bulk comes from fossil fuels at present. This type of hydrogen is called grey hydrogen.
Types of Vehicles based on Hydrogen:
- There are various types of Electric Vehicles that would be run using hydrogen. There are various categories of these vehicles:
- HEVs or Hybrid Electric Vehicles use high fuel economy and low tailpipe emission.
- Battery Powered Electric Vehicles use fully electric, rechargeable batteries with no petrol.
- Plug In Hybrid Vehicles use batteries plus petrol
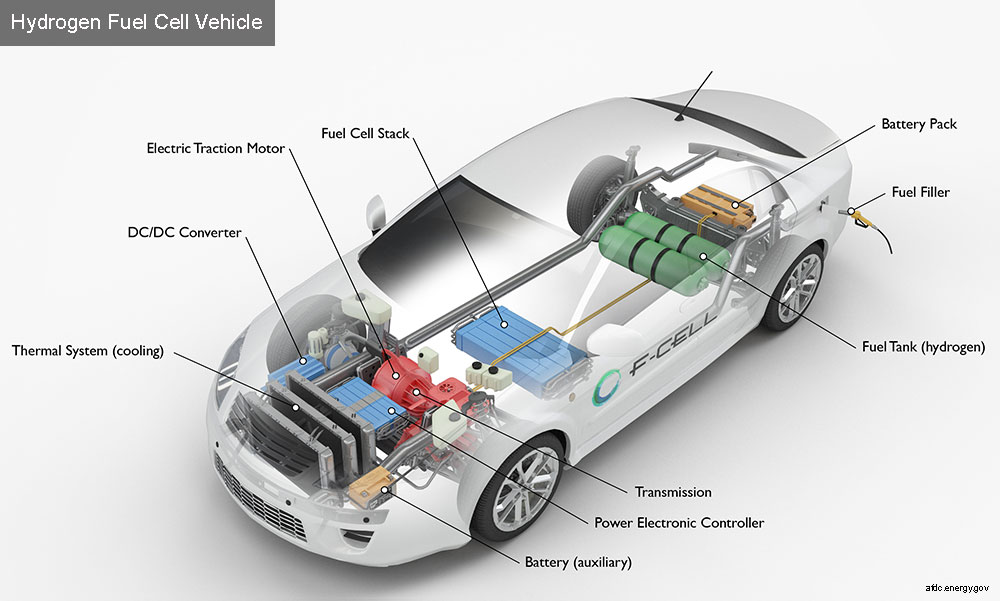
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles use hydrogen plus oxygen as fuel. These are fully electric but are not rechargeable like Battery powered electric vehicles.
Take a look at a hydrogen vehicle below:
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Advantages of Hydrogen fuel
- It has near zero carbon footprint. The electricity to extract hydrogen comes from fossil fuels.
- It can be stored in tanks such as CNG and can be integrated into car’s be,lies.
- The average that can be provided is about 500 kilometre or 400 miles per charge.
- It is lighter than heavy Lithium ion batteries, better for long haul trucks and commercial vehicles.
- It can be refueled in 5 minutes.
National Hydrogen Energy Mission: Disadvantages of Hydrogen fuel
- It has only three manufacturers that are equipped with the technology- Honda, Toyota and Hyundai. Under 25000 hydrogen FCEVs on road were launched in 2020, compared to EVs.
- Lack of Infrastructure: There are less than 500 hydrogen stations globally
- Hydrogen has great explosion risk and is a highly combustible gas.
Hydrogen is one of the most abundant elements on the earth. The global demand for hydrogen as a fuel has become thrice of what it was in 1975. It is also the only source of energy that only emits water vapour and leaves no residue in the air. Due to these advantages hydrogen is being seen as the biggest source of clean energy fuel in the near future.